As the poultry industry continues its shift toward sustainable, antibiotic-free production systems, managing gut health is becoming increasingly complex. Emerging challenges are reshaping how nutritionists, veterinarians, and producers approach intestinal health.
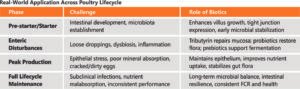
One of the most critical issues is microbial dysbiosis and leaky gut diarrhea in the post-antibiotic era. With reduced reliance on antimicrobial growth promoters, poultry flocks are more susceptible to imbalances in gut microbiota, leading to an increased prevalence of opportunistic pathogens and chronic enteric conditions. Additionally, early-life gut development is receiving growing attention. The first 7–10 days post-hatch represent a critical window for microbial colonization, immune priming, and intestinal morphogenesis. Any disruption during this stage—whether due to poor brooding, inadequate nutrition, or environmental stress—can impair gut function throughout the bird’s life.
Feed components such as mycotoxins, oxidized fats, and anti-nutritional factors (e.g., soy agglutinins) induce oxidative stress, alter microbiota, disrupt tight junctions and mucin layers, and initiate low-grade inflammation that compromises gut barrier integrity (“leaky gut”) in poultry. Subclinical infections with Clostridium further exacerbate epithelial damage, causing villus atrophy and apoptosis while increasing tight junction permeability—undermining mucosal defenses and predisposing flocks to secondary bacterial infections. Rising resistance to standard anticoccidials worsens Eimeria-induced mucosal injury, impairing nutrient absorption and causing wet litter issues. Moreover, environmental and management stressors—heat, overcrowding, transport, feed changes—interfere with mucin secretion and gut-brain axis signaling, promoting barrier disruption and dysbiosis. Finally, rapid batch turnover limits time for microbial stabilization, leading to inconsistent gut health and heightened cycle-to-cycle vulnerability.
These evolving challenges highlight the urgent need for advanced, holistic strategies focused on intestinal resilience. Approaches involving a synergistic blend of probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics—ideally delivered through next-generation technologies like GEH (Gastrointestinal Environment Harmonization)—are emerging as promising solutions for ensuring optimal gut functionality and performance under modern production pressures.
Understanding Biotics in Livestock and Poultry Nutrition
The concept of integrating “biotics”—namely prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, and synbiotic—has emerged as a cornerstone in modern poultry nutrition. As the industry moves away from antibiotic dependence due to rising antimicrobial resistance, the modulation of gut microbiota offers a sustainable and effective alternative for promoting intestinal integrity and overall productivity.
 Each biotic category offers a distinct yet complementary function:
Each biotic category offers a distinct yet complementary function:
- Prebiotics, such as MOS and XOS, are fermentable oligosaccharides that fuel beneficial microbes.
- Probiotics, like Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus clausii, and Clostridium butyricum, populate the gut with beneficial bacteria, outcompeting pathogens.
- Postbiotics, particularly tributyrin, deliver bioactive metabolites that reinforce gut barrier function and immune modulation.
- Synbiotics strategically pair pre- and probiotics to maximize colonization and metabolic synergy.
 This comprehensive framework supports intestinal health, nutrient utilization, immune defence, and microbial balance—foundational pillars for poultry performance.
This comprehensive framework supports intestinal health, nutrient utilization, immune defence, and microbial balance—foundational pillars for poultry performance.
Scientific Parameters for Selecting Effective Biotic Solutions
To ensure reliable and reproducible results in poultry systems, the selection of biotic-based interventions must be grounded in scientific rigor. The following parameters are critical:
- Gastrointestinal & Processing Stability: Functional strains must survive pelleting temperatures, feed storage conditions, and transit through the acidic stomach.
- Mechanism of Action: Each biotic’s action site (foregut vs. hindgut) and its physiological effect—e.g., anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, or epithelial restorative—must be defined and validated.
- Targeted Bioavailability: For molecules like tributyrin, targeted delivery to the ileum and ceca is essential. Triglyceride-bound butyrate derivatives ensure site-specific release.
- Safety & Regulatory Compliance: All bioactives must be species-specific, non-toxic, and compliant with poultry regulations, backed by performance and safety trials.
 Tributyrin: A Technologically Advanced Postbiotic for Poultry
Tributyrin: A Technologically Advanced Postbiotic for Poultry
Among postbiotics, tributyrin has emerged as a superior form of butyric acid due to its enhanced stability, controlled release, and site-specific activity. Unlike free or salt forms, tributyrin is odourless and efficiently bypasses upper GIT absorption, delivering bioactive butyrate directly to the lower intestine.
Core Benefits of Tributyrin
- Reinforces tight junctions and prevents intestinal permeability.
- Reduces gut inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Inhibits harmful pathogens by lowering intestinal pH.
- Promotes villus development and nutrient absorption, improving FCR and weight gain.
- Supports gut health under stress conditions (e.g., necrotic enteritis, dysbiosis).
A Functional Triad for Gut Health: Probiotics + Prebiotics + Postbiotics
The integration of probiotics, combined with prebiotics and tributyrin (a postbiotic), offers a scientifically advanced, multi-pronged approach to optimizing gut health in poultry. This unique combination delivers beneficial microbes, microbial substrates, and bioactive metabolites—all essential for promoting intestinal development, maintaining gut homeostasis, and preventing pathogen overgrowth.
Why This Combination Stands Out
Unlike conventional products that target only one aspect of gut health, this combination simultaneously enhances microbial balance, epithelial integrity, and intestinal functionality, ensuring a robust gastrointestinal environment capable of withstanding production-related stresses.
GEH Technology: Gastrointestinal Environment Harmonization
The effectiveness of this triad is significantly amplified when encapsulated using GEH Technology—a next-generation innovation that ensures precise delivery, enhanced stability, and optimal functionality of biotic components within the gastrointestinal tract.
GEH Technology Advantages
- Precision Targeting: Directs actives to specific gut sites (ileum, ceca).
- Controlled Release: Ensures sustained delivery of actives like tributyrin.
- Process Stability: Protects microbial and postbiotic functionality during pelleting and storage.
- Synergy Enhancement: Promotes cooperative interactions between biotics for optimal gut resilience.
Conclusion: From Science to Sustainability
This triadic approach powered by GEH technology offers poultry producers a scientifically validated, antibiotic-alternative solution to optimize gut health across life stages. By combining microbial intelligence with biochemical precision, this platform ensures sustained productivity, improved bird welfare, and enhanced economic returns—all through harmonization of the gastrointestinal environment.
by Dr. Kalyani Sarode, Optima Life Sciences









