 Balancing Tradition and Innovation: Understanding Conventional Feed Production Practices in India’s Livestock and Poultry Sectors
Balancing Tradition and Innovation: Understanding Conventional Feed Production Practices in India’s Livestock and Poultry Sectors
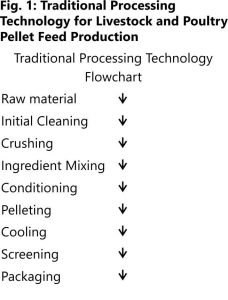
The production of pellet feed for livestock and poultry involves a defined process, as illustrated in Figure 1. Initially, raw materials undergo cleaning to remove impurities, followed by crushing for consistency. These materials are then mixed with essential ingredients, conditioned to enhance nutritional value, and formed into pellets. After cooling and quality screening, the pellets are packaged for distribution.
In India, this method reflects standard practices in the poultry and livestock sectors, utilizing locally sourced grains, oilseeds, and supplements to create nutrient-rich feed. This feed is crucial for the health and productivity of livestock and poultry, key components of India’s agricultural economy. As the population grows, so does the demand for high-quality pellet feed, prompting innovations in feed processing technologies to meet the needs of farmers and producers.
Challenges in Feed Production in the Indian Context
Issues with Oil Addition:
Fats, whether naturally occurring or added, are essential for enhancing pelleting efficiency. However, when fat content exceeds 3%, it can negatively impact pellet feed quality by reducing hardness and interfering with starch gelatinization, ultimately compromising both the quality and yield of the pellets.
However, when fat content exceeds 3%, it can negatively impact pellet feed quality by reducing hardness and interfering with starch gelatinization, ultimately compromising both the quality and yield of the pellets.
Low Conditioning Temperature and Formation Rate:
Maintaining the right moisture and heat balance during conditioning is crucial for producing high-quality pellets. The ideal moisture content for optimal pelleting performance is between 16% and 17%. However, variations in raw material composition can lead to challenges such as low conditioning temperatures and inadequate moisture, resulting in poor pellet formation rates.
 High Fines Rate:
High Fines Rate:
While there is no industry-wide consensus on the impact of starch gelatinization on poultry feed, it is generally accepted that improved gelatinization enhances pellet quality, reduces fines, and boosts feed conversion rates. Reducing the fines rate is crucial for improving feed efficiency, thereby enhancing performance in India’s poultry and livestock sectors.
Analysis of Problems – Evaluation of Pelleting Factor
The pelleting characteristics of raw materials vary significantly, necessitating specific pelleting conditions tailored to each material’s properties. Understanding how different raw materials influence 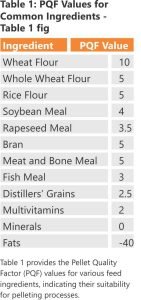 pellet quality is essential for producing high-grade feed.
pellet quality is essential for producing high-grade feed.
For instance, wheat flour has excellent pelleting properties, while materials high in fiber or minerals can pose challenges. To assess pelleting performance, each raw material is assigned a Pellet Quality Factor (PQF) on a scale from 0 to 10, with 10 indicating optimal performance. Negative PQF values signify materials that degrade pellet quality.
By systematically evaluating PQF, feed producers can make informed decisions about formulation and processing, optimizing feed quality and addressing the challenges of diverse raw materials. This analysis ultimately enhances pellet feed quality and supports the growth of India’s poultry and livestock industry.
Evaluation of Feed Pellet Quality Factor (FPQF) for Optimal Pellet Quality
The Feed Pellet Quality Factor (FPQF) is a crucial metric for feed mills assessing pellet quality. An FPQF value between 4.7 and 5.0 generally indicates the ability to produce high-quality pellets, though values above 5 may be needed for consistent premium quality. Some mills can maintain acceptable quality with an FPQF below 4.7, influenced by factors like material granularity and conditioning conditions. Notably, production lines using advanced equipment, such as expanders (super conditioners), may achieve acceptable quality with a lower FPQF due to their enhanced processing efficiency.
The FPQF is calculated using the following formula:
FPQF = (PQF₁ × η₁) + (PQF₂ × η₂) + (PQF₃ × η₃) + … + (PQFn × ηn)
Where:
PQF represents the Pellet Quality Factor for each ingredient in the feed formula.
η represents the percentage contribution of each ingredient to the overall formula.
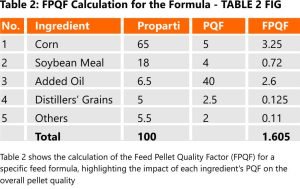
By calculating the FPQF for the feed formula used by the company, we can derive insights into the impact of ingredient composition on pellet quality, as shown in Table 2. This analysis helps optimize feed formulations, ensuring that the final pellet product meets the desired quality standards.
This systematic approach to evaluating FPQF enables feed mills to fine-tune their production processes and achieve consistent, high-quality output, improving the performance of the feed in India’s poultry and livestock sectors.
Expanded Pelleting Technology for Livestock and Poultry Feed Processing
The processing flow of expanded pelleting is shown in Figure 2:
 Integrating an extruder with a pellet mill significantly enhances feed processing efficiency, performance, and quality compared to traditional methods. This approach employs an expander (super-conditioner) that allows for greater flexibility in processing diverse raw materials while preserving nutritional value, efficacy of active ingredients, and feed safety.
Integrating an extruder with a pellet mill significantly enhances feed processing efficiency, performance, and quality compared to traditional methods. This approach employs an expander (super-conditioner) that allows for greater flexibility in processing diverse raw materials while preserving nutritional value, efficacy of active ingredients, and feed safety.
The key advantage of this system is its improved conditioning and expansion of feed ingredients, which enhances nutrient digestibility and absorption, benefiting livestock and poultry health and productivity. Additionally, it enables precise control over processing parameters, allowing for customized formulations to meet specific nutritional and production goals.
poultry health and productivity. Additionally, it enables precise control over processing parameters, allowing for customized formulations to meet specific nutritional and production goals.
However, the simultaneous operation of the expander and pellet mill requires greater equipment stability and coordination. Effective synchronization of these components is essential for maximizing processing efficiency and maintaining consistent product quality, thereby fully leveraging this advanced technology.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional Processing vs. Extrusion Expansion Pelleting Technology
The shift from traditional feed processing to extrusion expansion pelleting technology represents a significant advancement, addressing long-standing challenges in feed production. Integrating an expander with a pellet mill allows for better control over moisture and heat, leading to improved feed quality and overall production efficiency.
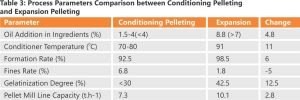
A comparative analysis of process parameters before and after implementing this technology, detailed in Table 3, shows notable optimization in feed production methods. This transition not only enhances performance but also paves the way for the future of feed manufacturing by more effectively meeting the rising nutritional demands of livestock and poultry.
In India, adopting expanded pelleting technology has significant potential to boost productivity and profitability in the livestock and poultry industry. By utilizing this advanced processing method, feed manufacturers can improve the nutritional quality and safety of feed products, contributing to the overall growth and sustainability of the agricultural sector.
Conclusions
Advantages of Extrusion Expansion Pelleting Technology in Livestock and Poultry Feed Production
The implementation of extrusion expansion pelleting technology in livestock and poultry feed production offers numerous benefits, marking a new era of efficiency and quality. Key advantages include:
Expanded Raw Material Selection: This technology allows for a broader range of raw materials, enhancing formulation flexibility and reducing reliance on specific ingredients.
Cost Reduction: Its versatility enables the use of cost-effective ingredients, lowering formula costs and improving economic feasibility for producers.
Improved Animal Digestibility and Conversion Rate: Enhanced conditioning and expansion processes lead to superior digestibility and better feed conversion rates, improving overall livestock and poultry performance.
 Enhanced Feed Hygiene: Advanced processing techniques improve feed hygiene, ensuring the safety and health of animals.
Enhanced Feed Hygiene: Advanced processing techniques improve feed hygiene, ensuring the safety and health of animals.
Increased Liquid Feed Addition: The technology allows for the incorporation of liquid feed components, promoting better nutrient absorption and feed palatability.
Enhanced Feed Quality and Capacity: It elevates feed quality by preserving nutritional integrity and optimizing pellet hardness, while also increasing production volumes to meet demand.
Energy Savings: Streamlined processing leads to energy savings, supporting sustainability efforts within the feed industry.
With a national focus on reducing feed grain dependency and exploring alternative resources, extrusion expansion pelleting technology is likely to gain significant traction among feed enterprises. Its promotion and application will be crucial for enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness in India’s livestock and poultry feed sector.
by Mr. Rex, Vice President, South Asia and Mr Arun Kumar, Country Head, India, Famsun.









